Dublin Analytical Education
The Science of Chocolate Melt Viscosity Testing: A Comprehensive Guide
In Summary
Chocolate viscosity measurement ensures smooth texture and consistent mouthfeel. ICA Method 46 is the industry standard for assessing flow behaviour in chocolate production. Dublin Analytical supplies viscometers and rheometers suitable for this testing.
What is Chocolate Melt Viscosity Testing and Why is it Important?
Chocolate melt viscosity testing is a critical process in the chocolate industry, ensuring that molten chocolate has the right flow properties for manufacturing and quality control. It determines the ease with which chocolate can be transported, coated, dipped, or moulded, directly impacting the final product’s texture and mouthfeel.
How Do Rheological Properties of Chocolate Affect Processing and Quality?
Rheology is the study of flow and deformation properties of materials. In chocolate manufacturing, the rheological properties of chocolate dictate how it behaves under stress and at different temperatures. Understanding these properties helps manufacturers optimise production processes and achieve consistent product quality.
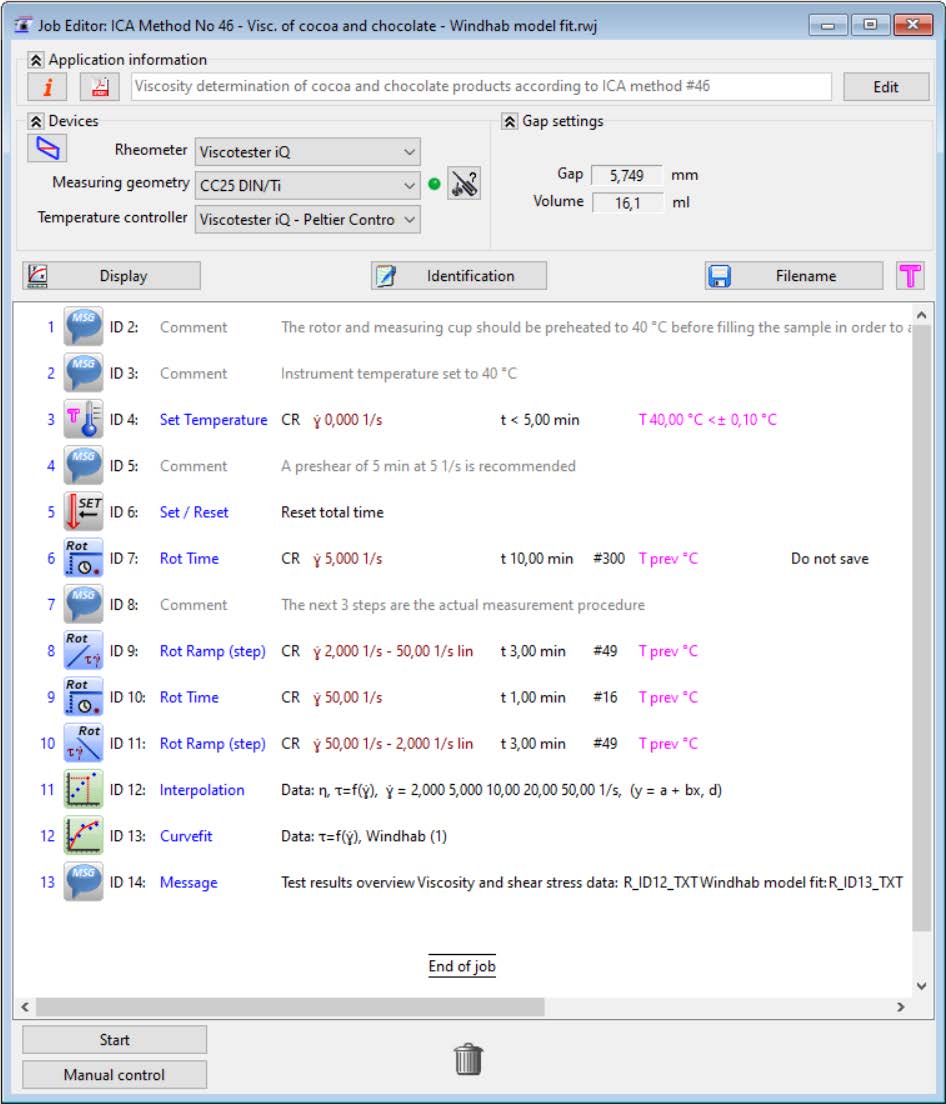
What is ICA Method 46 for Chocolate Viscosity Measurement?
The International Confectionery Association (ICA) Method 46 is a standard procedure used to measure the viscosity of molten chocolate at 40°C using a rotational rheometer with a coaxial cylinder measuring geometry.
This method provides a reproducible approach to evaluating chocolate flow properties under controlled conditions.
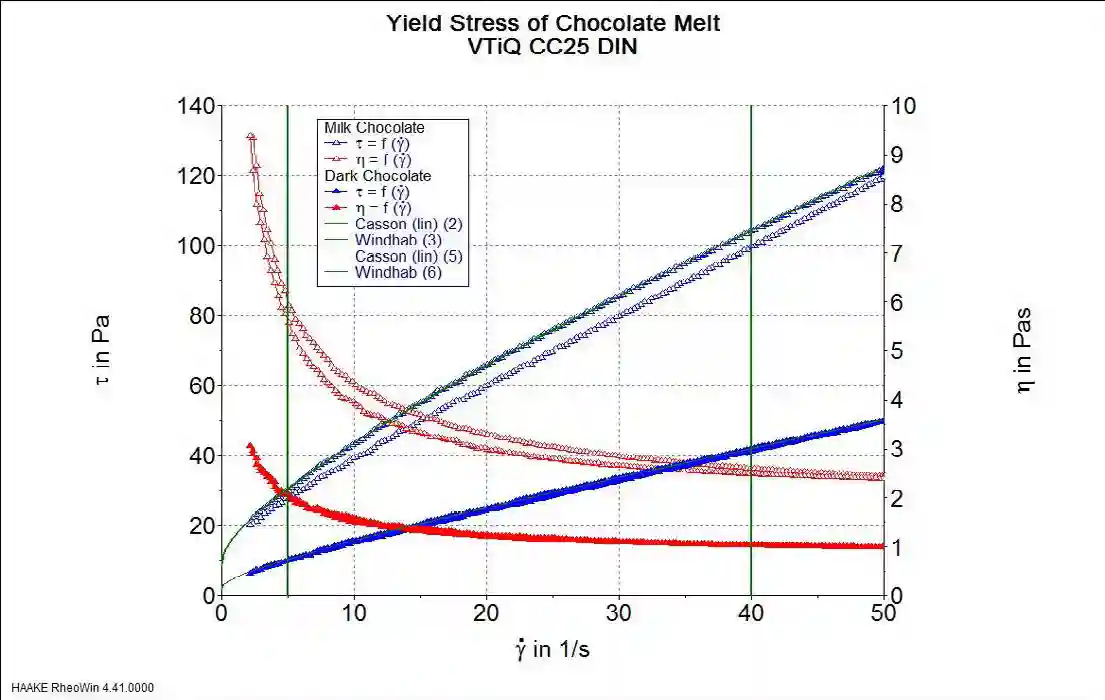
How is Chocolate Yield Stress Measurement Conducted?
Yield stress is a key parameter in chocolate processing, defining the force required to initiate flow. It is measured using rotational rheometers where chocolate samples are subjected to controlled stress conditions. The Servais method, Windhab model, and Casson model are commonly used for yield stress calculations.
What is Viscosity and Why is it Critical in Chocolate Processing?
Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to deformation under shear stress, or how easily it flows when a force is applied.
It is essential in processes such as piping, pumping, and enrobing, ensuring smooth production without blockages or inconsistencies. Shear viscosity is influenced by temperature, composition, and shear rate.
What is Thixotropy in Chocolate Melts?
Thixotropy refers to a time-dependent decrease in viscosity under constant shear stress.
In chocolate production, thixotropic behaviour ensures that chocolate remains workable while being processed but solidifies properly when left undisturbed.
How is Chocolate Rheometry Performed with Rotational Rheometers?
Rotational rheometers, such as the HAAKE Viscotester iQ, provide precise viscosity measurements. These devices operate by rotating a spindle or cylinder in molten chocolate, measuring the resistance encountered.
How is Chocolate Rheometry Performed with Rotational Rheometers?
Rotational rheometers, such as the HAAKE Viscotester iQ, provide precise viscosity measurements. These devices operate by rotating a spindle or cylinder in molten chocolate, measuring the resistance encountered.

Thermo HAAKE Viscotester iQ Rheometers
The Thermo HAAKE Viscotester iQ Rheometers are innovative instruments designed for precise measurement of rheological properties in various industries such as food, cosmetics, and petrochemicals.
What is the HAAKE Viscotester iQ and how is it Used in Chocolate Analysis?
The HAAKE Viscotester iQ is an advanced rheometer equipped with Peltier temperature control to maintain the required 40°C testing temperature. It enables detailed viscosity profiling and yield stress analysis, ensuring high-precision results in chocolate quality control.
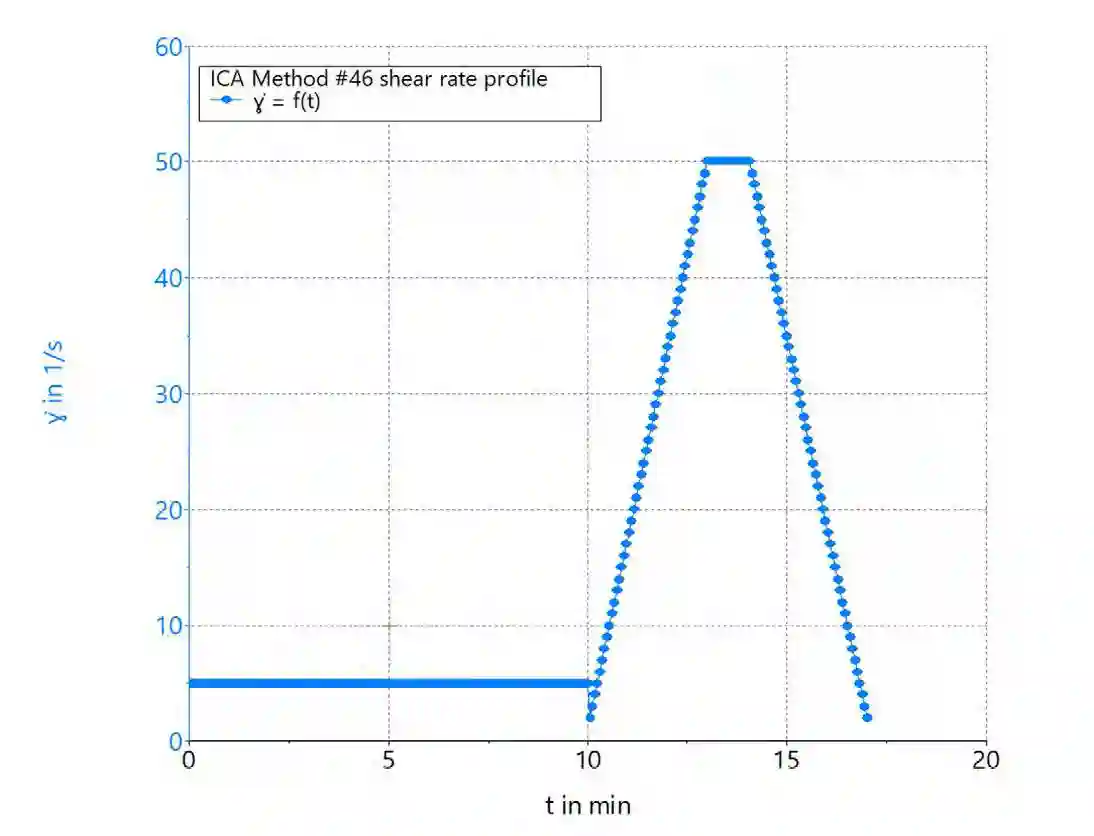
What is the Shear Rate Profile in Chocolate Viscosity Testing?
The shear rate profile defines how viscosity changes as shear rate increases. ICA Method 46 applies a stepwise shear rate increase from 2 s-1 to 50 s-1, followed by a steady hold phase and a controlled decrease. This approach allows operators to assess chocolate’s structural response to varying flow conditions.
How Do the Windhab and Casson Models Explain Chocolate Flow?
The Windhab and Casson models are mathematical equations used to describe the flow behaviour of chocolate melts:
- Casson Model: Estimates yield stress and shear-thinning behaviour.
- Windhab Model: Provides a more advanced analysis of complex chocolate flow properties.
Both models help predict chocolate behaviour under different processing conditions.
How is High-Precision Chocolate Viscosity Measurement Achieved?
High-precision viscosity measurement requires:
- Accurate temperature control (Peltier modules in rheometers)
- Standardised testing methods (ICA Method 46)
- Reproducible sample preparation
- Advanced data analysis (HAAKE RheoWin software for automated evaluation)
How Do Dark and Milk Chocolate Differ in Viscosity?
- Milk Chocolate: Higher viscosity due to increased milk fat and sugar content, leading to more resistance to flow.
- Dark Chocolate: Lower viscosity due to higher cocoa content and lower sugar concentration.
These differences impact processing methods and final product characteristics.
What Role Does Shear Stress Play in Chocolate Processing?
The Windhab and Casson models are mathematical equations used to describe the flow behaviour of chocolate melts:
- Casson Model: Estimates yield stress and shear-thinning behaviour.
- Windhab Model: Provides a more advanced analysis of complex chocolate flow properties.
Both models help predict chocolate behaviour under different processing conditions.
How Does Temperature Control Affect Chocolate Rheology?
Temperature is a major factor in chocolate viscosity. Even small variations can significantly alter flow properties. Peltier-controlled rheometers provide precise temperature regulation, ensuring consistent results during testing.
How is Quality Control of Chocolate Ensured Using Viscosity Testing?
Viscosity testing ensures:
- Uniform texture and consistency
- Efficient production and processing
- Reliable coating and dipping performance
- Compliance with industry standards
Manufacturers rely on viscosity measurements to maintain high-quality chocolate products.
What to do next?
Interested in optimising your chocolate production? Explore our range of high-precision rheometers and enhance your quality control process today! You can also reach out to one of our Product Managers for a personalised demonstration.
FAQ's
The ICA Method 46 is the industry standard for chocolate viscosity testing, using rotational rheometers at 40°C.
Higher temperatures reduce viscosity, making chocolate more fluid. Precise Peltier temperature control is essential for accurate testing.
Yield stress measures the force required to initiate flow. Higher yield stress results in thicker, more structured chocolate.
Milk chocolate has higher viscosity due to increased milk fat and sugar content, whereas dark chocolate is generally more fluid.
Viscosity testing ensures consistent texture, proper coating, and efficient manufacturing, helping manufacturers maintain high product standards.
Contact Us Today
We take great pleasure in assisting you and ensuring you get a prompt response to your questions
Live chat opening hours Mon – Fri 9:15 to 16:30 (UK Time)